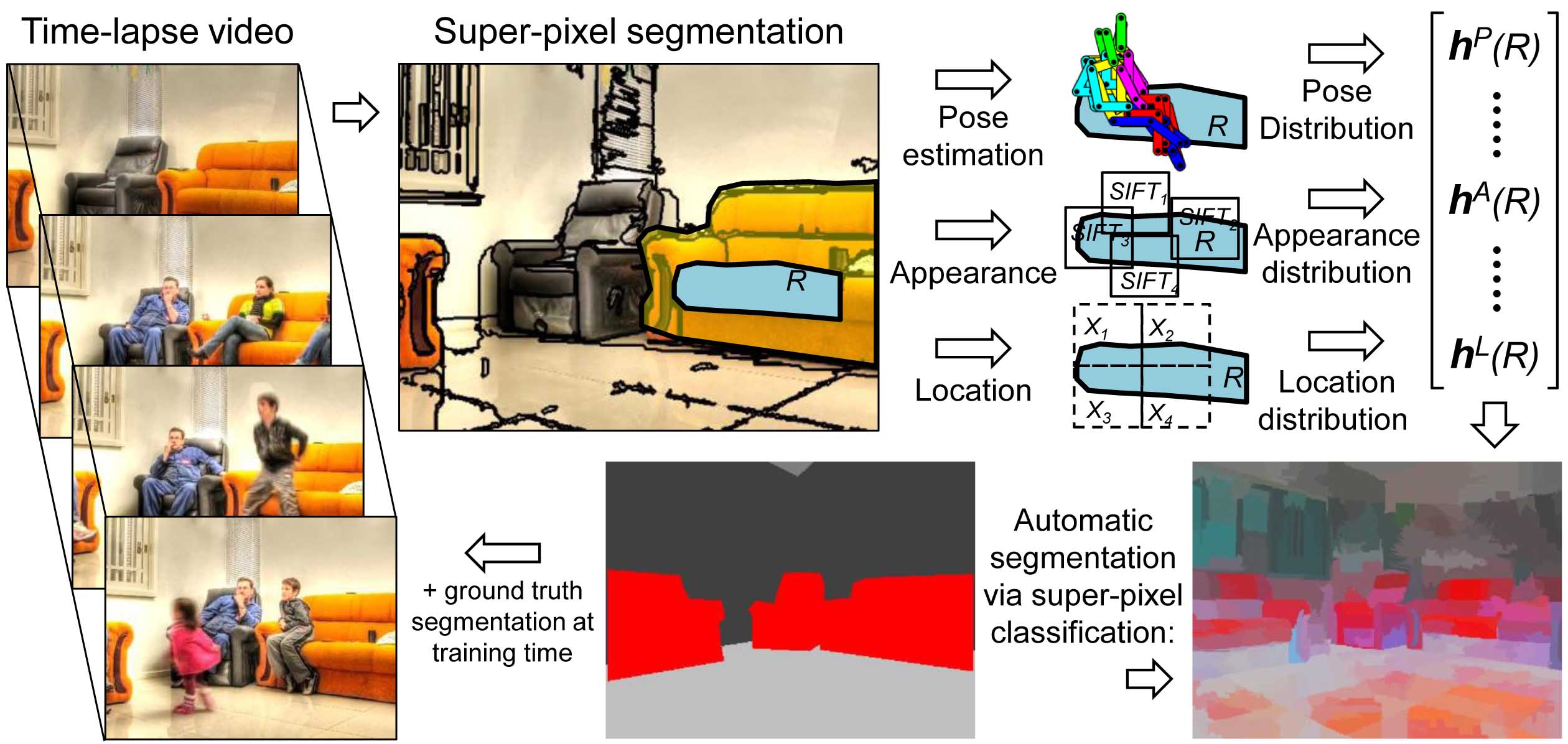
Scene semantics from long-term observation of people
People
Abstract
Our everyday objects support various tasks and can be used by people for dirent purposes. While object classification is a widely studied topic in computer vision, recognition of object function, i.e., what people can do with an object and how they do it, is rarely addressed. In this paper we construct a functional object description with the aim to recognize objects by the way people interact with them. We describe scene objects (sofas, tables, chairs) by associated human poses and object appearance. Our model is learned discriminatively from automatically estimated body poses in many realistic scenes. In particular, we make use of time-lapse videos from YouTube providing a rich source of common human-object interactions and minimizing the ert of manual object annotation. We show how the models learned from human observations significantly improve object recognition and enable prediction of characteristic human poses in new scenes. Results are shown on a dataset of more than 400,000 frames obtained from 146 time-lapse videos of challenging and realistic indoor scenes.
Paper

|
ECCV Paper / Poster Citation BibTeX @inproceedings{delaitre2012,
author = {Delaitre, V. and Fouhey, D. and Laptev,
I. and Sivic, J. and Gupta, A. and Efros, A.},
title = {Scene semantics from long-term observation of people},
booktitle = {Proc. 12th European Conference on Computer Vision},
year = {2012},
}
|
Dataset and Code
- Scene semantics source code (5.4Mb) : code used to compute results reported in the paper.
- Database (2.4Mb) : code for downloading the 146 videos dataset.
- Pose detections (743Mb) : pose detections used in the paper.
- Pose detectors (167Mb) : code and data for training the pose detectors.
- Ground truth pose annotations (400Kb) : over 1500 annotated poses (at least 10 per video).
Extended Results
- Segmentation results for different method over all videos.


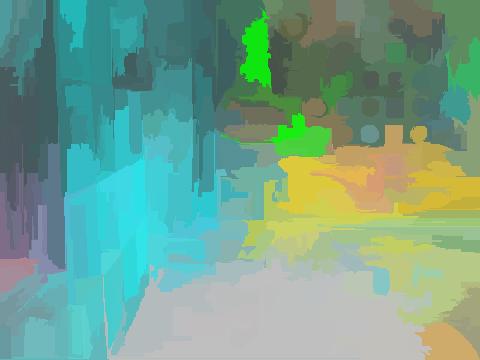




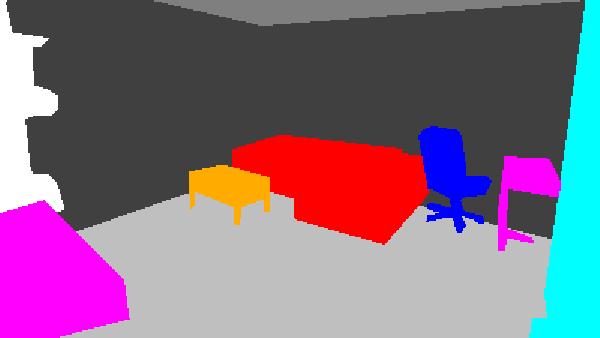

- Spatial locations of objects relative to the 6 most contributing poses for all labels:
Sofa / Armchair 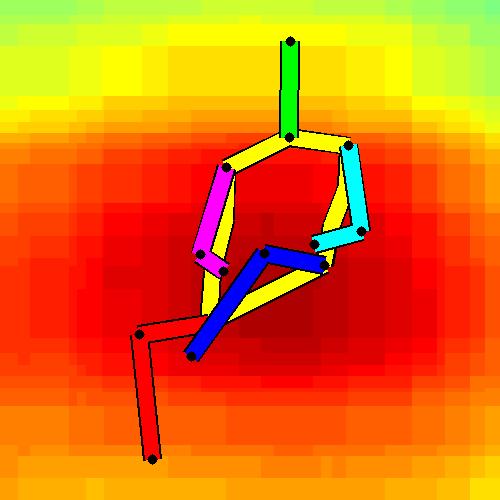
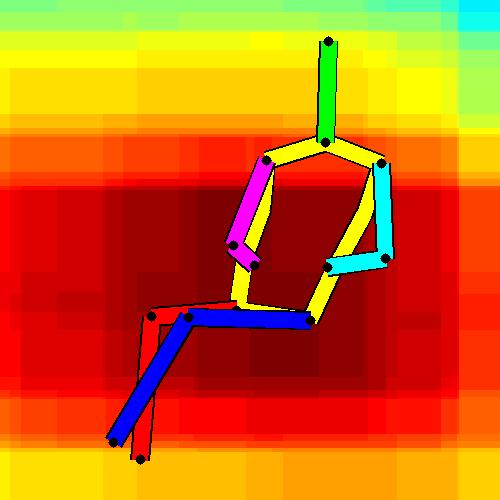
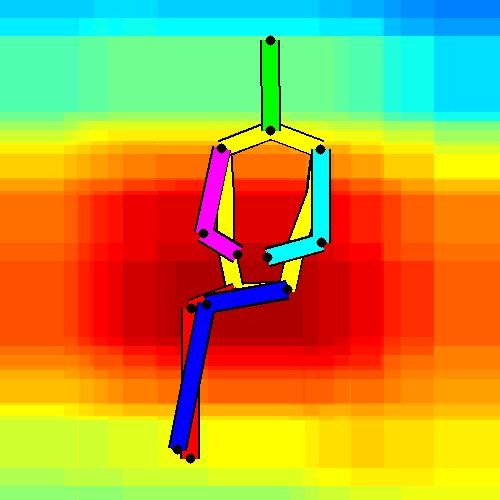
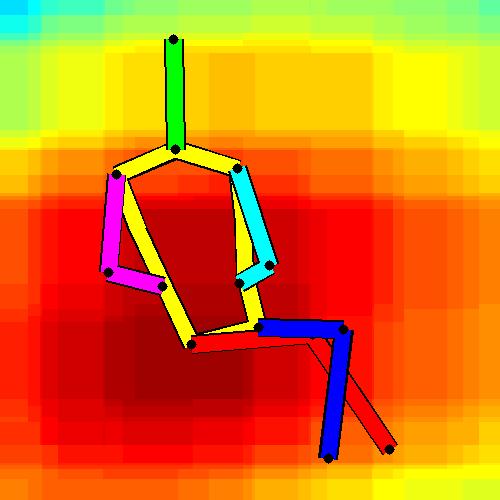
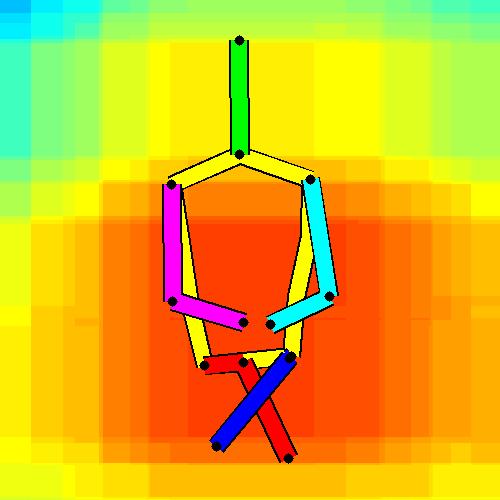
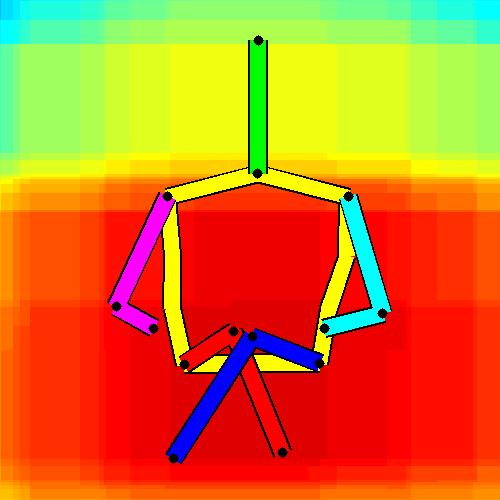
Table 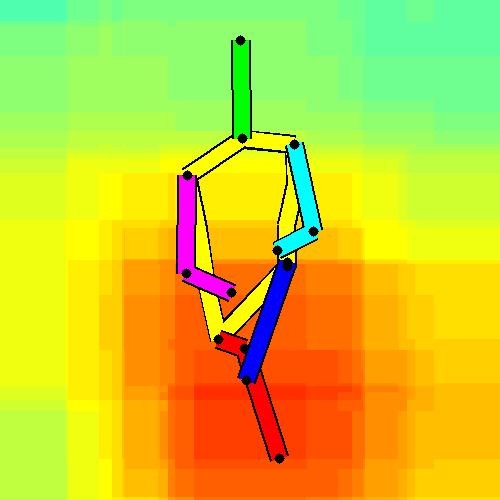
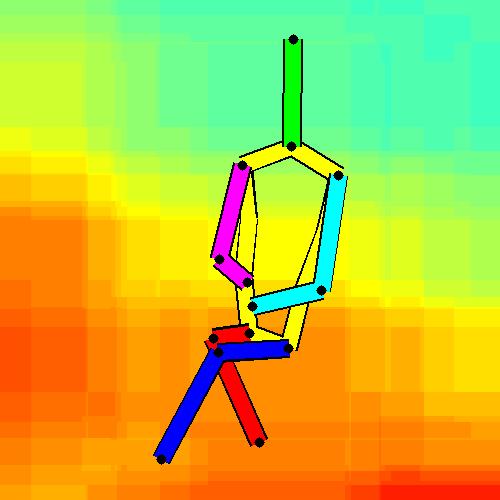
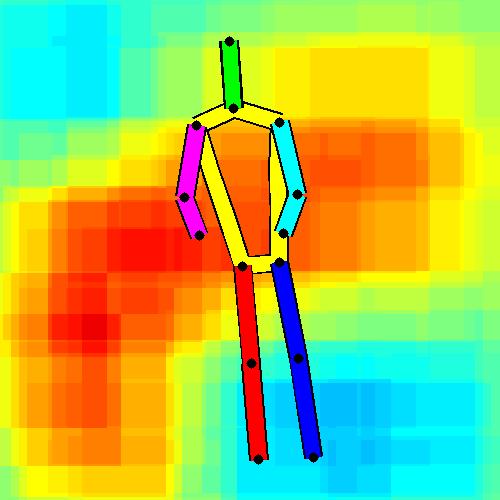
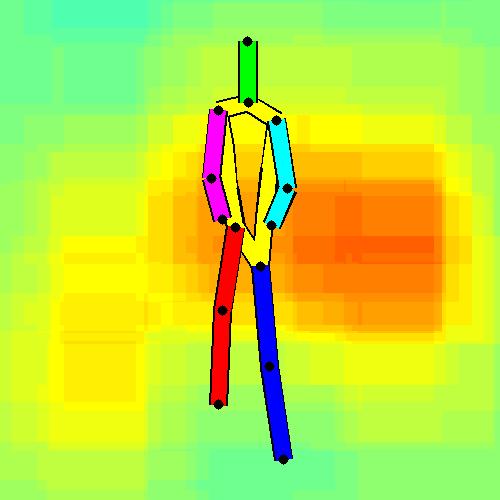
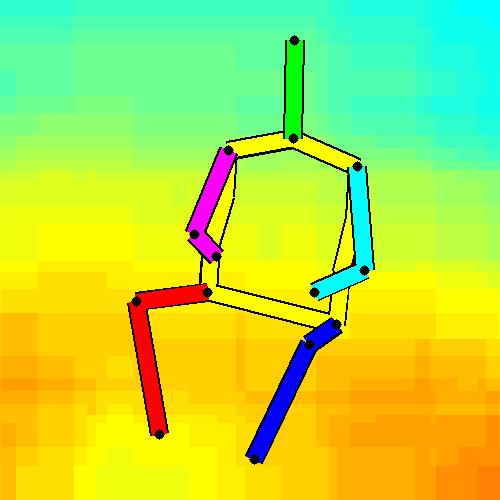
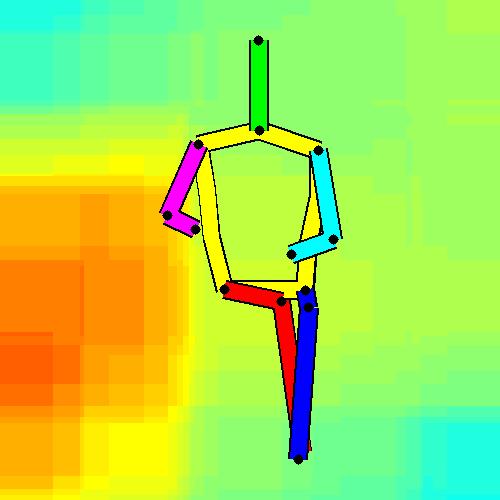
Cupboard 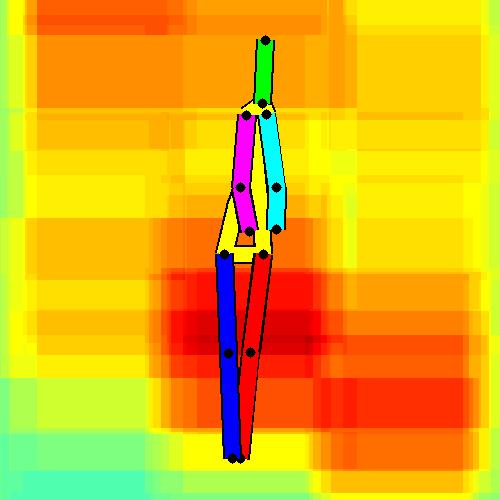
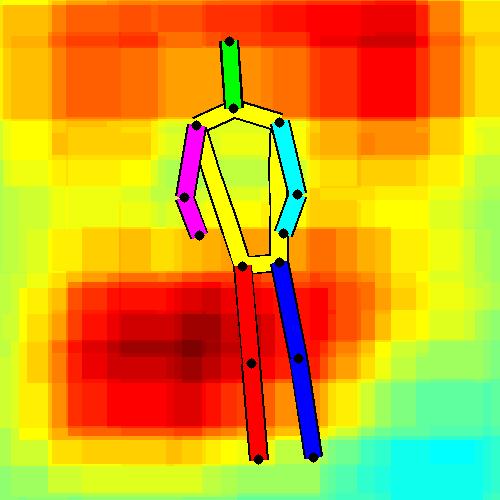

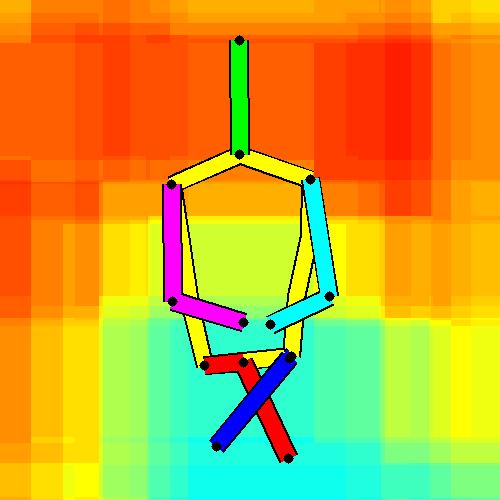
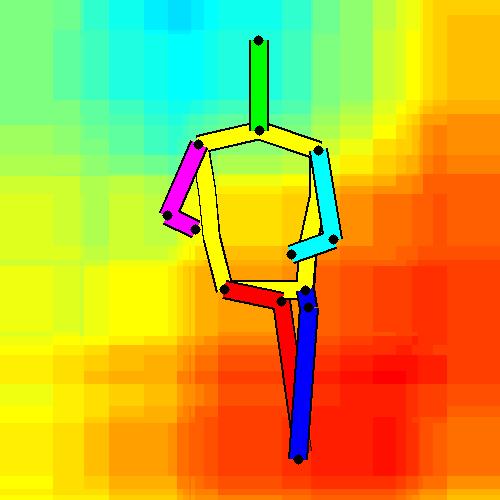
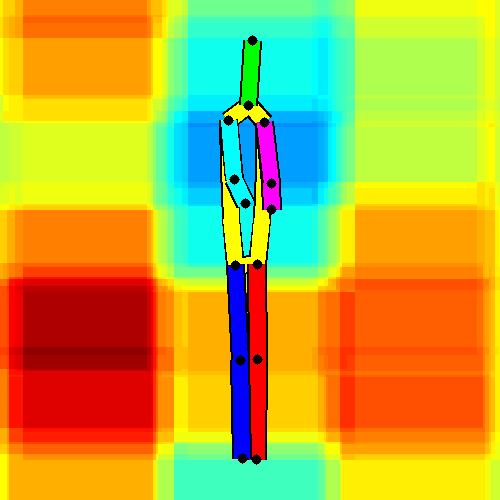
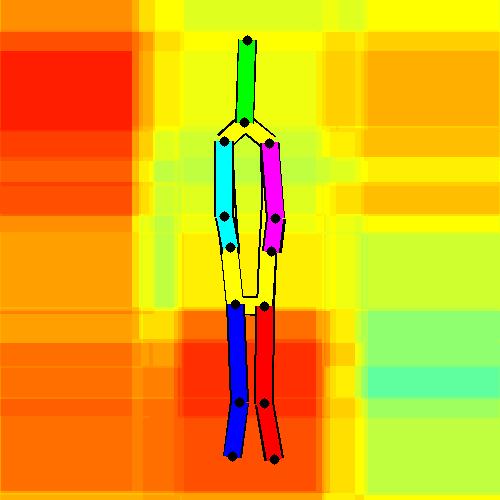
Related Works
Funding
This research is supported by:
- NSF Graduate Research Fellowship for David Fouhey
- ONR-MURI Grant N000141010934
- Qauero
- OSEO
- MSR-INRIA
- EIT-ICT
- ERC Grant Videoworld
Copyright Notice
The documents contained in these directories are included by the contributing authors as a means to ensure timely dissemination of scholarly and technical work on a non-commercial basis. Copyright and all rights therein are maintained by the authors or by other copyright holders, notwithstanding that they have offered their works here electronically. It is understood that all persons copying this information will adhere to the terms and constraints invoked by each author's copyright.