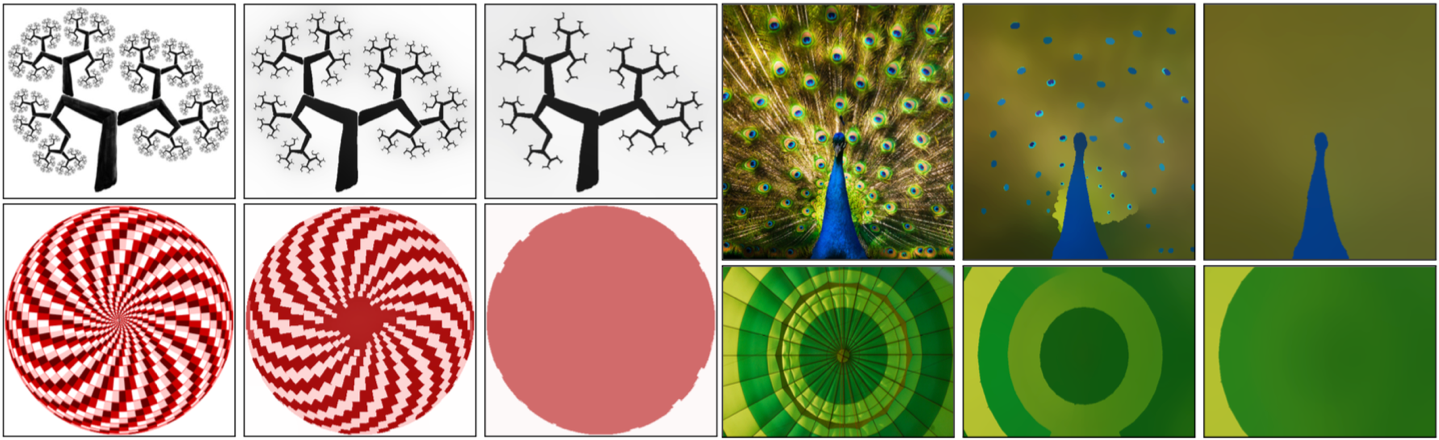
 |
Figure 1. An example of SD filtering for scale-space representation.
Paper

B. Ham, M. Cho, J. Ponce
Robust Image Filtering Using Joint Static and Dynamic Guidance
Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2015)
PDF | Abstract | BibTeX | Supplementary Material (16MB)
Robust Image Filtering Using Joint Static and Dynamic Guidance
Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2015)
PDF | Abstract | BibTeX | Supplementary Material (16MB)
Abstract
Regularizing images under a guidance signal has been used in various tasks in computer vision and computational photography, particularly for noise reduction and joint upsampling. The aim is to transfer fine structures of guidance signals to input images, restoring noisy or altered struc- tures. One of main drawbacks in such a data-dependent framework is that it does not handle differences in structure between guidance and input images. We address this problem by jointly leveraging structural information of guidance and input images. Image filtering is formulated as a nonconvex optimization problem, which is solved by the majorization-minimization algorithm. The proposed algorithm converges quickly while guaranteeing a local minimum. It effectively controls image structures at different scales and can handle a variety of types of data from different sensors. We demonstrate the flexibility and effectiveness of our model in several applications including depth super-resolution, scale-space filtering, texture removal, flash/non-flash denoising, and RGB/NIR denoising.BibTeX
@InProceedings{ham2015,
author = {Bumsub Ham and Minsu Cho and Jean Ponce},
title = {Robust Image Filtering using Joint Static and Dynamic Guidance},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition},
year = {2015}
}

B. Ham, M. Cho, J. Ponce
Robust Guided Image Filtering Using Nonconvex Potentials
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (2017)
PDF | Abstract | BibTeX
Robust Guided Image Filtering Using Nonconvex Potentials
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (2017)
PDF | Abstract | BibTeX
Abstract
Filtering images using a guidance signal, a process called guided or joint image filtering, has been used in various tasks in computer vision and computational photography, particularly for noise reduction and joint upsampling. This uses an additional guidance signal as a structure prior, and transfers the structure of the guidance signal to an input image, restoring noisy or altered image structure. The main drawbacks of such a data-dependent framework are that it does not consider structural differences between guidance and input images, and that it is not robust to outliers. We propose a novel SD (for static/dynamic) filter to address these problems in a unified framework, and jointly leverage structural information from guidance and input images. Guided image filtering is formulated as a nonconvex optimization problem, which is solved by the majorize-minimization algorithm. The proposed algorithm converges quickly while guaranteeing a local minimum. The SD filter effectively controls the underlying image structure at different scales, and can handle a variety of types of data from different sensors. It is robust to outliers and other artifacts such as gradient reversal and global intensity shift, and has good edge-preserving smoothing properties. We demonstrate the flexibility and effectiveness of the proposed SD filter in a variety of applications, including depth upsampling, scale-space filtering, texture removal, flash/non-flash denoising, and RGB/NIR denoising.BibTeX
@InProceedings{ham2015,
author = {Bumsub Ham and Minsu Cho and Jean Ponce},
title = {Robust Guided Image Filtering Using Nonconvex Potentials},
booktitle = {IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence},
year = {2017}
}
Code
